
Cold chain management and monitoring are crucial components of the logistics and supply chain industries. Cold chain logistics refers to the transportation, storage, and handling of temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals, food, and beverages. Cold chain management ensures that the products maintain their quality, potency, and safety by controlling their temperature at all stages of the logistics process. Monitoring is the process of tracking the temperature of products at different points in the supply chain to ensure that they remain within the required temperature range. In this complete guide to cold chain management and monitoring, we will discuss what a cold chain is, the types of the cold chain, what is transported through a cold chain, temperature standards for cold chain logistics, the principles of a cold chain, how a cold chain is different from a supply chain, cold chain technologies, important of cold chain, and cold chain monitoring technologies.
Complete Guide to Cold Chain Management and Monitoring
What Is a Cold Chain?

A cold chain is a temperature-controlled logistics process that involves the transportation, storage, and handling of products that require refrigeration or freezing to maintain their quality, efficacy, and safety. Cold chain logistics is essential in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and beverages, where temperature-sensitive products must be transported across the supply chain while maintaining their temperature range.
Types of Cold Chain

In the Cold Chain industry products can range from food, pharmaceuticals, vaccines, blood, and other medical products that require temperature control to maintain their quality and efficacy. The cold chain consists of a series of steps and storage facilities that maintain specific temperatures and humidity levels to ensure that these products remain safe and effective. There are different types of cold chains, each with its specific requirements and applications. This article explores the various types of cold chain and their specific features.
Food Cold Chain
Food cold chain management is crucial in the food and beverage industry. It involves the storage, transportation, and distribution of perishable goods, including fresh fruits and vegetables, meat, dairy products, and frozen foods. The food cold chain typically begins at the farm, where produce is harvested and transported to processing facilities under temperature-controlled conditions. The products are then transported to distribution centers, supermarkets, and restaurants under refrigerated or frozen conditions. The cold chain helps to preserve the quality, freshness, and nutritional value of the food products, ensuring that they remain safe and fit for human consumption.
Pharmaceutical Cold Chain
The pharmaceutical cold chain is a specialized type of cold chain that is designed to ensure that drugs and vaccines maintain their potency during storage and transportation. The pharmaceutical cold chain typically begins at the manufacturing facility, where drugs and vaccines are produced under strict quality control conditions. The products are then stored and transported under strict temperature-controlled conditions, typically between 2 to 8 degrees Celsius for vaccines and between 15 to 25 degrees Celsius for most drugs.
The pharmaceutical cold chain includes specialized equipment such as refrigerated trucks, cold rooms, and insulated containers to maintain the required temperature during transportation. Any de““`viation from the recommended temperature range can lead to a loss of potency, rendering the products ineffective or even dangerous. Therefore, strict temperature monitoring and control are essential in the pharmaceutical cold chain to ensure that the products remain safe and effective.
Blood Cold Chain
The blood cold chain is a specialized type of cold chain that is designed to ensure that blood and blood products remain safe and effective during storage and transportation. Blood products, including red blood cells, platelets, and plasma, are highly perishable and require temperature-controlled storage and transportation. The blood cold chain typically begins at the collection center, where blood is collected from donors and processed under strict quality control conditions.
The products are then stored and transported under strict temperature-controlled conditions, typically between 1 to 6 degrees Celsius. The blood cold chain includes specialized equipment such as refrigerated trucks, cold rooms, and insulated containers to maintain the required temperature during transportation. Any deviation from the recommended temperature range can lead to a loss of quality and effectiveness, rendering the products unsuitable for transfusion.
What Products Are Transported Through a Cold Chain?
Various products are transported through a cold chain, including pharmaceuticals, biologics, vaccines, fresh produce, meat, dairy, seafood, and frozen food products. These products require temperature control during transportation, storage, and handling to prevent spoilage, degradation, or bacterial growth.
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals are one of the most commonly transported products through a cold chain. These products are sensitive to temperature fluctuations and can become ineffective or dangerous if not stored and transported at the appropriate temperature. Vaccines, insulin, blood products, and other biologics must be stored and transported between 2°C and 8°C to maintain their efficacy and safety.
Fresh Produce
Fresh produce, such as fruits and vegetables, are also transported through a cold chain. These products are typically transported in refrigerated trucks or containers to maintain their freshness and prevent spoilage. The temperature range for fresh produce varies depending on the product, but most fruits and vegetables require temperatures between 0°C and 5°C.
Meat, Dairy, and Seafood
Meat, dairy, and seafood are other products that require temperature control during transportation and storage. These products are often transported in refrigerated trucks or containers to prevent bacterial growth and maintain freshness. The temperature range for meat, dairy, and seafood varies depending on the product, but most require temperatures between 0°C and 5°C.
Frozen Food Products
Frozen food products, such as frozen meals, vegetables, and seafood, are also transported through a cold chain. These products must be stored and transported at temperatures below -18°C to prevent spoilage and maintain their quality. Frozen food products are typically transported in refrigerated trucks or containers equipped with freezers.
Maintaining low temperatures to preserve perishable goods is a crucial aspect of cold chain logistics management. However, it is essential to note that not all cold chain cargo requires sub-zero temperatures for transportation. For instance, during winter, some fruits and vegetables need to be kept warm to preserve their texture or extend their shelf life. This highlights the need for different temperature and ambient conditions to maintain various types of cold chain cargo, leading to cold chain logistics being alternatively referred to as temperature-controlled transport or cool chain logistics. An enhanced visibility platform with ERP integration and the ability to provide accurate, useful data is required to manage cold chain logistics successfully.
Temperature Standards for Cold Chain Logistics

The temperature standards for cold chain logistics vary depending on the type of product being transported or stored. Regulatory bodies and industry associations have established guidelines for temperature control to ensure the quality and safety of temperature-sensitive products. Some of the temperature standards for cold chain logistics include:
- Vaccines: Vaccines must be stored and transported between 2°C and 8°C to maintain their efficacy and safety.
- Biologics: Biologics, such as blood products and insulin, must be stored and transported between 2°C and 8°C.
- Fresh Produce: Fresh produce, such as fruits and vegetables, must be stored and transported between 0°C and 5°C to maintain their freshness and prevent spoilage.
- Meat, Dairy, and Seafood: Meat, dairy, and seafood must be stored and transported between 0°C and 5°C to prevent bacterial growth and maintain freshness.
- Frozen Food Products: Frozen food products, such as frozen meals and vegetables, must be stored and transported at temperatures below -18°C to prevent spoilage and maintain their quality.
The ability to transport goods within specific temperature ranges would have been a challenging task without the advancements in techniques and technologies that enable temperature-controlled packing materials and shipping conditions.
Temperature-controlled transportation options provide contemporary businesses with the assurance and flexibility to establish global supply chains for perishable goods that require specific temperature conditions.
What are the Principles of Cold Chain Management

The principles of cold chain management are crucial for maintaining the integrity of these products and ensuring that they reach their destination in optimal condition.
Temperature control: The primary principle of cold chain management is temperature control. Temperature-sensitive products must be maintained within a specific temperature range to prevent spoilage or degradation. This involves monitoring and controlling the temperature during transportation and storage, using specialized refrigeration systems and temperature-monitoring devices.
Proper handling: Proper handling of temperature-sensitive products is essential to prevent damage and contamination. This involves using appropriate packaging materials, such as insulated containers and cooling packs, to maintain the required temperature. Additionally, products must be handled carefully during transportation and storage to prevent physical damage or exposure to harmful substances.
Regular monitoring: Regular monitoring of the temperature and other conditions during transportation and storage is critical for ensuring that products remain within the required temperature range. This involves using temperature-monitoring devices, such as data loggers, to track temperature fluctuations and identify any potential issues that may affect the quality and safety of the products.
Training and education: Proper training and education of personnel involved in cold chain management are crucial for ensuring that the principles of temperature control, proper handling, and regular monitoring are followed correctly. This includes training on the use of specialized refrigeration systems, packaging materials, and temperature-monitoring devices, as well as best practices for handling and transporting temperature-sensitive products.
Quality control: Quality control measures must be in place to ensure that products meet the required standards of quality and safety. This involves conducting regular inspections and quality checks, as well as implementing corrective actions if any issues are identified.
What Cold Chain Technologies Are Used Today?

Over the years, the management of temperature-sensitive products has been an important concept, and the technologies involved have undergone significant advancements. Today, the technologies employed in cold chain transport can be broadly classified into the following categories.
Cold Chain Warehouse Storage Technologies
- Deep Freezer
- Walk-in Freezer
- Walk-in-coolers
Cold Chain Transit Storage Technologies
- Reefers- are trucks or containers designed with active cooling technology through battery-powered or other refrigeration systems, making them suitable for transporting large quantities of goods over road, rail, or sea.
- Air freight containers- are specifically designed to comply with the mandates for airline freight and can accommodate smaller expedited cold chain shipments.
- Ice Lined Refrigerators (ILR)- are cold-retaining, highly insulated containers that employ passive cooling. They are lined with coolants that rely on their cooling capacity to keep the products chilled
Technologies for Cold Chain Cooling or Techniques for Temperature Control

- Phase Change Materials (PCM).
- Evaporative cooling.
- Cooling materials like dry ice, ice, liquid nitrogen, gel packs, etc.
Active Cooling
- Reefers — are transportable refrigeration units that are powered by fuel or battery packs.
- In situations where a power supply is not available or is unreliable, absorption or compression refrigerators/freezers are the preferred option.
Cold Chain Packaging Technologies
- Insulators are essential components in cold chain logistics, which include thermal blankets, specialized foam, cold insulation bags, and Vacuum Insulated Panels (VIP).
- “Dry” or “wet” shippers are vessels specially designed with compartments for liquid nitrogen, making them suitable for transporting frozen products.
- Specialized cold box or cool box containers called cryoboxes or polystyrene containers can be customized for certain cargo requirements. These containers are typically made of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) or Expanded Polyurethane (EPU).
- Active containers are portable reefers that are highly compact, making them ideal for use in cold chain logistics.
Different Types of Transportation Options

Businesses have a variety of transportation options available when it comes to cold chain logistics. In order to make the best decision for their needs, business owners must carefully consider their options. Some of the most common transportation options are trucks, trains, airplanes, and ships.
- Trucks are an efficient way for businesses to transport large quantities of goods over long distances. They are cost-effective because they can carry larger loads than other modes of transportation and can access locations that may be difficult for other vehicles.
- Trains provide businesses with a great way to transport cargo quickly and efficiently over long distances due to their size and lower fuel costs compared to trucks. Additionally, trains can make multiple stops along a route, giving businesses greater flexibility in planning their transportation needs.
- Airplanes offer businesses a faster option for traveling between destinations in different countries or continents. While air travel is more expensive than other transportation modes, it can save money in the long run if products are time-sensitive or require multiple stops during transit.
- Lastly, ships provide businesses with a cost-effective way to transport large volumes of goods over vast distances. Although ships generally take longer than other modes of transportation, they can save money on fuel costs due to their greater carrying capacity compared to smaller vehicles such as trucks or planes.
Efficient tracking mechanisms
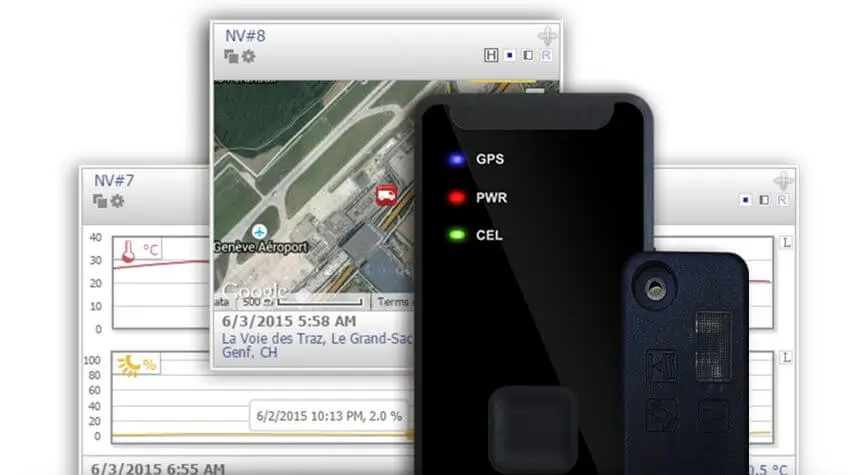
Establishing a robust tracking system is crucial to maintaining transparency and ensuring efficiency in cold chain logistics. Companies must prioritize the implementation of a tracking system that provides real-time updates and complete visibility into the progress of shipments and deliveries. This enables customers to track their orders and stay informed about their status, which results in a positive user experience.
To establish an effective tracking system, companies must consider various factors. Firstly, they must determine the appropriate method for tracking shipments and deliveries. This could include GPS devices for vehicles on the road, IoT-enabled asset trackers, or the use of RFID technology for warehouse tracking. Additionally, companies must evaluate the type of information that needs to be tracked and stored to provide clients with relevant updates regarding their orders. Furthermore, they must ensure that they have user-friendly software that facilitates easy data storage and retrieval.
Efficiency is a key factor in developing an effective tracking system. Companies can leverage automation techniques to streamline manual processes such as generating reports or updating customer accounts with new information. Automation reduces manual labor, saving time while gathering data points efficiently and accurately.
Finally, security is a critical consideration when setting up a tracking mechanism. Companies must ensure that all data is securely stored and encrypted to prevent unauthorized access by third parties or malicious actors. This safeguards client privacy and upholds the company’s reputation during transit processes.
Using Monitoring Services

To ensure the safety and quality assurance of cold chain logistics, utilizing monitoring solutions is a recommended strategy. With the help of monitoring solutions, businesses and organizations can easily track progress and ensure that goals are being met in a timely and efficient manner.
Data loggers and asset trackers are some examples of monitoring solutions that can help identify potential risks and issues early on by providing detailed data that can be analyzed. These solutions offer critical insights into the overall performance of the journey, enabling teams to make necessary adjustments to their plans accordingly and stay on track.
Automated alerts are also a key feature of monitoring solutions. They notify teams whenever there is an issue or if immediate attention is required, allowing for proactive actions to be taken. This approach helps ensure that the product remains viable and within the correct conditions throughout its journey.
You can keep track of all of your international cold chain shipments with LIBERO from ELPRO, or you can include temperature data into your ERP. The data logger automatically generates a PDF report at the destination describing the temperature exposure during shipping.
By implementing monitoring solutions, businesses and organizations can effectively guarantee the safety and quality assurance of their cold chain logistics while achieving their desired goals in the most efficient and effective manner.
Analyzing the Information Gathered in Transit

Analyzing the data collected during transit can provide organizations with critical insights into their supply chain operations, allowing them to optimize their processes for maximum efficiency. By leveraging the right data points, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their operations and identify any bottlenecks that may be hindering their performance. This information is essential for streamlining supply chain operations, maximizing resource utilization, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Collecting and analyzing data gathered during transit is particularly crucial in the cold chain sector, where product safety and security are top priorities. To achieve these objectives, businesses must develop effective logistics management systems that leverage the most suitable transportation options, tracking mechanisms, and monitoring solutions. These tools enable companies to track their shipments in real-time, identify potential issues before they become major problems, and take corrective actions quickly when necessary.
In summary, efficient logistics management is essential for keeping products safe and secure throughout the supply chain. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes transportation options, tracking mechanisms, monitoring solutions, and data analysis, businesses can optimize their supply chain operations and ensure the highest level of customer satisfaction. For expert guidance on navigating the complexities of cold chain logistics, reach out to Adapt Ideations today.
Which Cold Chain Monitoring Technologies Can You Use?
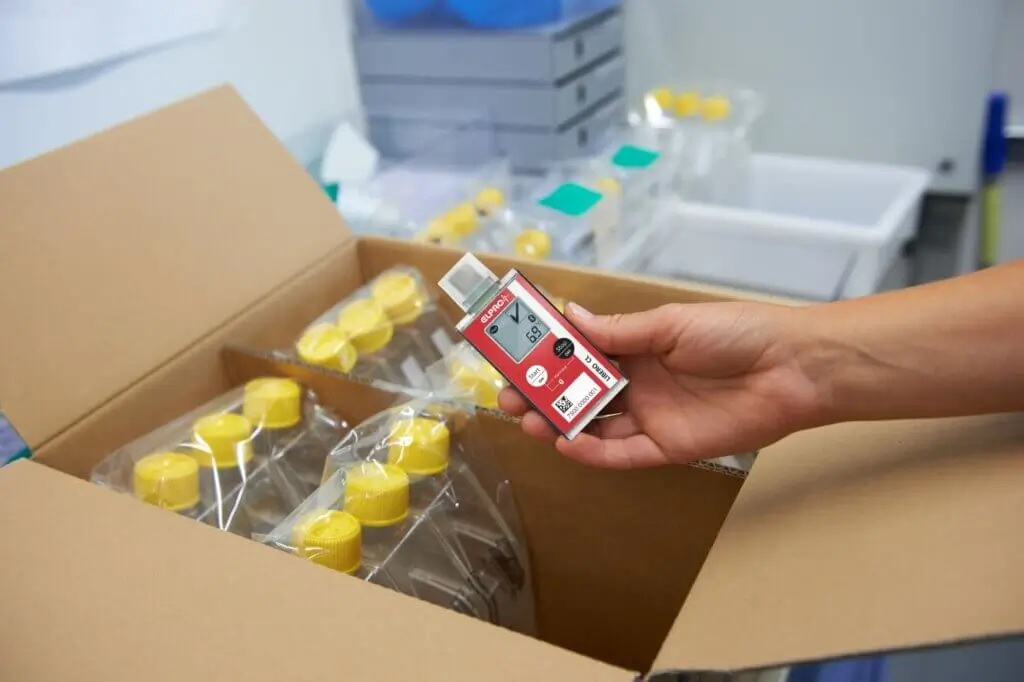

Effective management of the cold chain begins with temperature tracking. Transporters adopt various measures such as assessing risks of standard routes, using dedicated vehicles, implementing phase change gel bricks to detect excursions, or employing double packaging and active cooling to secure their shipments in order to minimize the likelihood of temperature spikes during transit.
Logistics companies now have more advanced technologies at their disposal to track and manage their cold chain operations. The most popular and effective temperature-tracking solutions for cold chains include:
- Infrared thermometers enable the user to measure surface temperature from a distance by scanning shipments.
- Wired digital thermometers involve placing sensors in the cold storage area and connecting them to a monitoring/logging device through wires. They are typically utilized to monitor shipments that require deep freeze or frozen conditions, where traditional temperature loggers may not function due to extreme cold.
- Temperature data loggers are currently the most commonly used temperature tracking solution in cold chain management. They are typically included as part of the cold chain shipment during transit and are categorized into the following types:
- Passive temperature loggers are battery-operated devices that record temperature data at predetermined intervals, which can be analyzed by downloading it through USB or other connectivity options.
- RFID or Bluetooth temperature data sensors also referred to as beacons, resemble passive temperature data loggers. They allow wireless access to their data, which makes them more convenient to use for large-scale operations.
Important of Cold Chain Management
Food safety: In the food and beverage industry, cold chain management is essential for ensuring that products such as meat, dairy, and fresh produce remain fresh and safe for consumption. Any break in the cold chain, such as a failure to maintain the required temperature during transportation or storage, can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria and spoilage, nny interruption in the cold chain may present a substantial threat to the health of consumers.
Medication efficacy: In the pharmaceutical industry, cold chain management is critical for ensuring that drugs and vaccines remain effective. Many medications require a specific temperature range to maintain their potency, and any deviation from this range can lead to a loss of efficacy. This can be particularly important in developing countries, where access to healthcare may be limited, and the availability of effective medications is crucial.
Cost savings: Effective cold chain management can also lead to cost savings for businesses. By ensuring that products remain in optimal condition, companies can reduce the amount of waste and spoilage, which can be a significant source of financial loss. Additionally, proper cold chain management can help to reduce the risk of product recalls and associated costs.
Compliance: Many industries, such as pharmaceuticals and medical devices, are subject to strict regulations and guidelines regarding the transportation and storage of their products. Proper cold chain management is critical for meeting these requirements and ensuring compliance with regulatory bodies.